Can freshwater plants and algae act as an effective feed supplement to reduce methane emissions from ruminant livestock?
March 01, 2024 | Science of The Total Environment |
Introduction: Livestock contribute significantly to global greenhouse gas emissions, with methane production being a major concern. The marine red algae, Asparagopsis taxiformis, has shown promise in inhibiting methane production in livestock as feed additives, but challenges in scaling up production exist. In this study, researchers from Deakin University explore Australian freshwater plants and algae as potential feed supplement with methane-inhibiting properties.
Key findings: Three algal mixes and one plant species (Montia australasica) demonstrated the potential to reduce methane emission in in vitro batch assays. The algal mixes, particularly one dominated by Spirogyra maxima, and M. australasica showed promising results, suggesting an optimum dose for methane reduction. Fatty acids in Algal mix 1 and flavonoids like apigenin and kaempferol in M. australasica were identified as potential contributors to methane reduction. Importantly, the mineral composition of these samples indicated their safety for livestock consumption at a 20% inclusion rate.
Read more
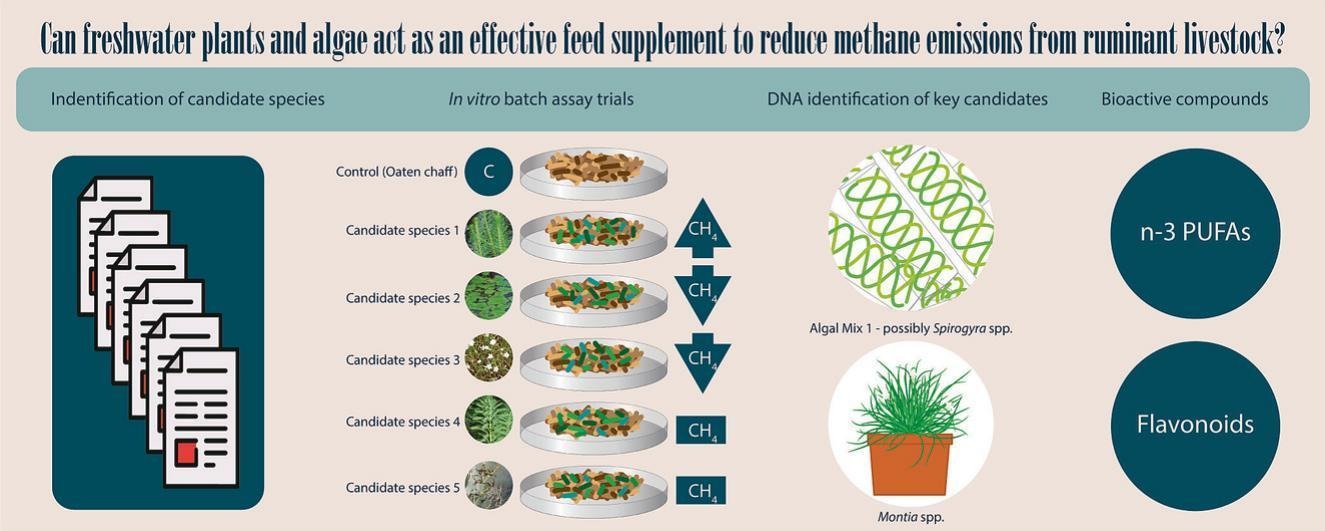
Fig. | Graphical Abstract.
Viewed Articles
March 01, 2024 | Science of The Total Environment |Â Â Introduction: Livestock contribute significantly to global greenhouse gas emissions, with methane production being a major concern. The marine red
Read More
January 15, 2022 | Atmosphere | Source |Â Introduction: Livestock both drives and suffers from climate change, contributing 14.5% of global GHG emissions while facing growing climate-induced stress. Re
June 24, 2024 | Humanities and Social Sciences Communications | Â Introduction: Digital inclusive finance is widely promoted as an enabler of green transitions, yet its environmental impacts in agricul
June, 2024 | Trends in Microbiology | Source | Â Introduction: Excessive nitrification in agroecosystems causes nitrate leaching and Nâ‚‚O emissions. Although nitrification inhibitors (NIs) reduce nitrog
June 23, 2022 | Science | Â Introduction: Without rapid changes to agriculture and food systems, the goals of the 2015 Paris Agreement will not be met. In this review, researchers led by the University
January 3, 2024 | Nature Communications | Source |Â Introduction: Conventional intensive farming boosts yields but also drives GHG emissions, soil degradation, and climate vulnerability, especially in






