World Resources Institute| Source | Download |
The "State of Climate Action 2023" report underscores the inadequacy of current global efforts to limit global warming to 1.5°C. The majority of indicators are off track, demanding immediate and intensified action. Out of the 42 assessed indicators, only electric vehicle adoption is on track for 2030 targets, the remainders are off track, and six indicators are regressing.
The food and agriculture sector, a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, needs transformation through supply- and demand-side shifts. Efforts should focus on reducing food loss, cutting meat consumption, and implementing sustainable farming practices. Despite positive developments, such as commitments to agricultural innovation and climate-friendly diets, global progress remains slow. Urgent action is required to achieve sustainable food production, mitigate emissions, and meet climate goals amidst the ongoing challenges in the food and agriculture sector.
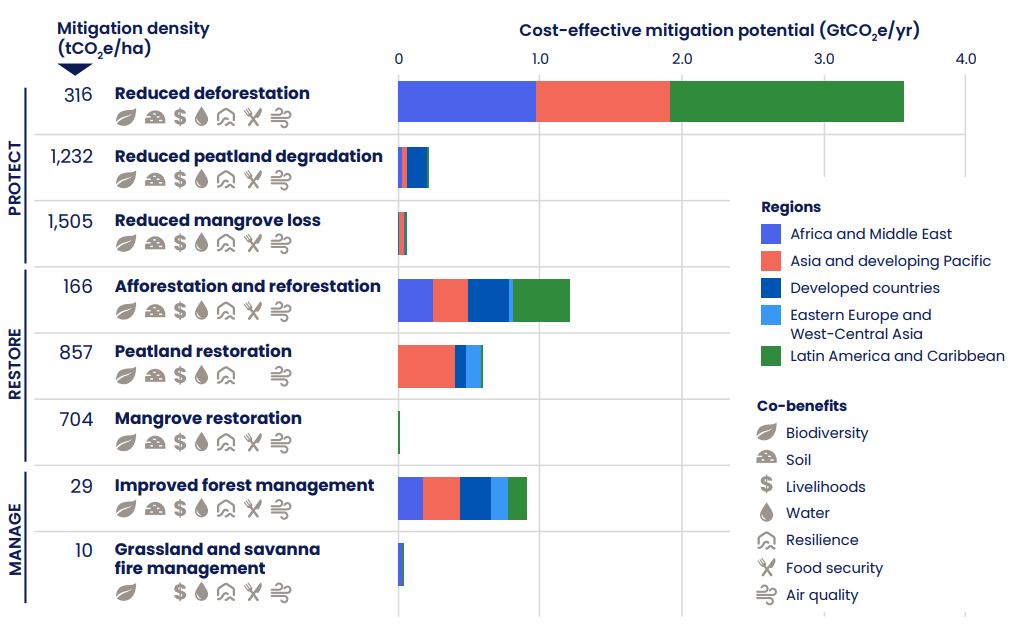
To limit global warming to 1.5°C, alongside substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, carbon removal technologies are crucial. This includes both natural approaches like forests and technological methods. However, the current scale of technological carbon removal falls far short, with less than 1% of the expected annual requirement achieved. While there's increased financial support and momentum in this area, challenges persist. These encompass the need for more public funding, deployment support, increased demand from buyers, attention to measurement and reporting accuracy, and addressing governance gaps to ensure responsible and equitable scaling of these technologies.
Fig. | Global cost-effective mitigation potentials for land-based measures across forests, peatlands, mangroves, and grasslands from 2020 to 2050.