Evaluating food supply chain emissions from Japanese household consumption
January 15, 2022 | Applied Energy |
Introduction: Household consumption, particularly eating habits, significantly impacts greenhouse gas emissions and thus climate change. However, there hasn't been a comprehensive analysis of the entire food supply chain and its environmental impact across different household segments. To fill this gap, an international team of researchers from University of Tokyo in Japan and various research institutes in China and UK uses a modified environmental input-output model to assess food-related carbon footprints in Japan.
Key findings: Results reveal that over 60% of the carbon footprint stems from food production, while wholesale and retail stages contribute about 38%. Interestingly, the wealthiest households exhibit the highest per capita carbon emissions across all food types, emphasizing income-based differences. In metropolitan areas like Kanto, dining out contributes significantly to emissions. Notably, red meat consumption substantially influences regional and income-based emission disparities. To mitigate household food carbon emissions, optimizing food supply chain management and promoting local consumption of fresh produce and meat are crucial strategies.
Read more
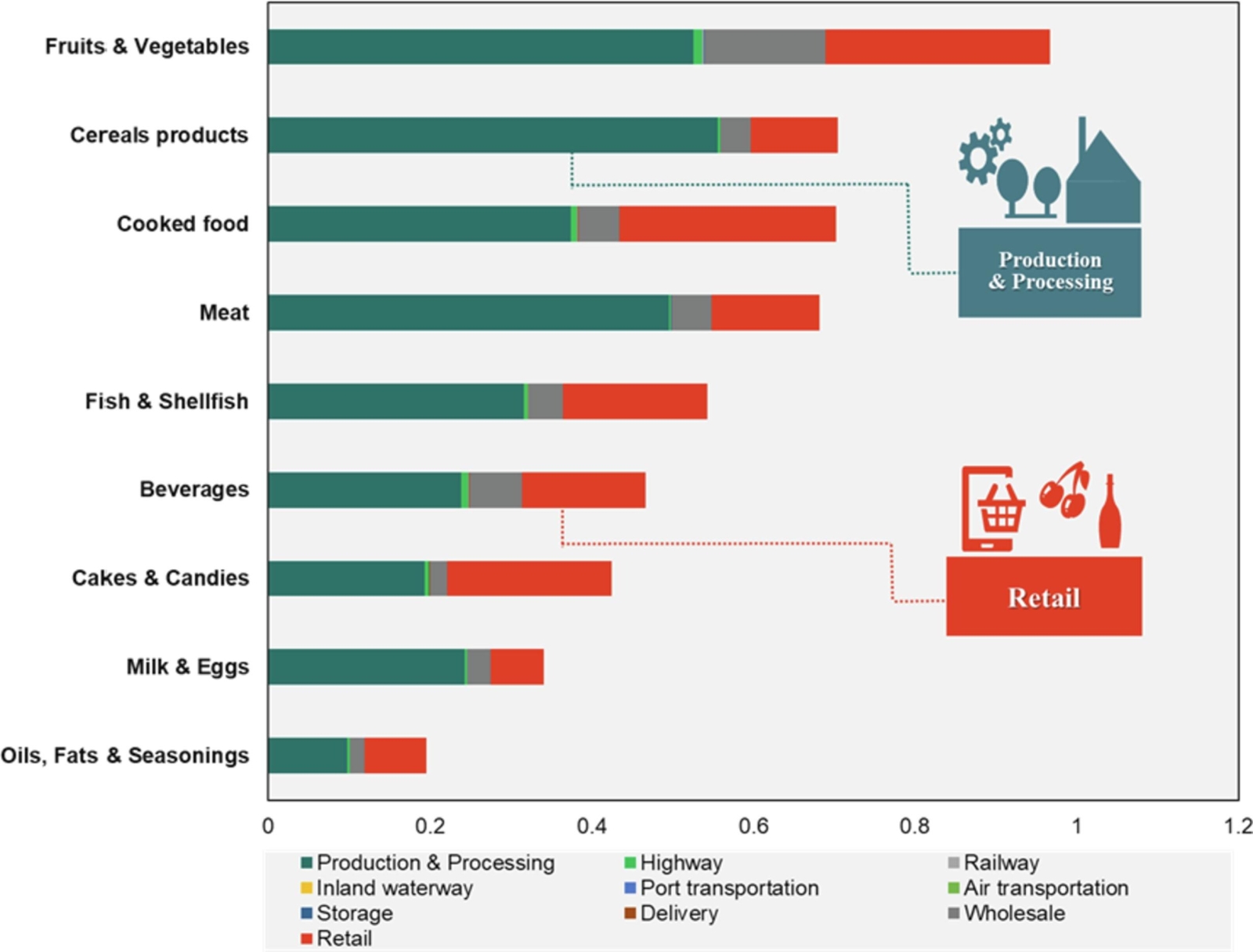
Fig. | Distribution of emissions along the food supply chain by food type (t CO2 per capita / year).
Viewed Articles
January 15, 2022 | Applied Energy |  Introduction: Household consumption, particularly eating habits, significantly impacts greenhouse gas emissions and thus climate change. However, there hasn't
Read More
August 27, 2020 | Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology |  Introduction: Led by an India-based team from Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya, the Indian Institute of Remote Sensing
March 2, 2022 | The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment | Source | Introduction: An Italy-based research team from the University of Tuscia and University of Rome conducted a systematic lit
March 16, 2020 | Nature Sustainability | Source | Introduction: Researchers from INRAE (France), Aarhus University (Denmark), and Chalmers University of Technology (Sweden) argue that conventional Lif
February 14, 2024 | Journal of Environmental Management |  Introduction: A research team from the University of Bologna and the University of Urbino Carlo Bo in Italy conducts a systematic mapping stu
June 5, 2023 | International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment | Source |  Introduction: The study, led by researchers from the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), investigates innovative too






