December 21, 2020 | Nature Food | Source |
Introduction: Environmental changes, from climate shifts to extreme events, threaten food systems globally, affecting production, distribution, and consumption. These impacts, exacerbated by globalization, demand a deeper understanding of their effects on food security. Researchers based in University of Delaware, Rutgers School of Public Health, and American University in the US explore how environmental variability propagates through supply chains, and based on the analysis propose measures to enhance resilience and inform policy and business decisions.
Key findings: Environmental variability impacts food supply chains at various entry points, predominantly during production. Rainfed agriculture and smallholders are especially vulnerable, facing risks like floods, droughts, and pests. These hazards affect food quantity, quality, and safety, leading to fluctuations in nutrient content, increased aflatoxin levels, and foodborne illnesses. Storage conditions also influence food safety, with extreme weather events exacerbating risks. Distribution and market access are disrupted by floods and extreme weather, impacting food trade and affordability. Consumption is affected by shifts in food availability, affordability, and quality, leading to changes in dietary intakes and nutritional outcomes. Environmental shocks propagate through supply chains, with most research focusing on staple crops and production shocks. Price fluctuations reveal the interconnectedness of supply chains, while responses to shocks vary across actors and supply chain stages.
Governments and private sectors can enhance resilience through irrigation, infrastructure improvements, and crop diversification. Food processing and fortification strategies can improve shelf life and nutritional quality. Supply chain actors need to collaborate to mitigate the impacts of environmental variability and avoid unintended consequences. Understanding food supply chain dynamics, surprises, and spillovers is crucial for enhancing resilience and sustainability in the face of simultaneous and unprecedented shocks, which are becoming more frequent due to climate change. Maintaining diversity in production and sourcing and integrating climate-smart strategies are essential for ensuring food security in the future.
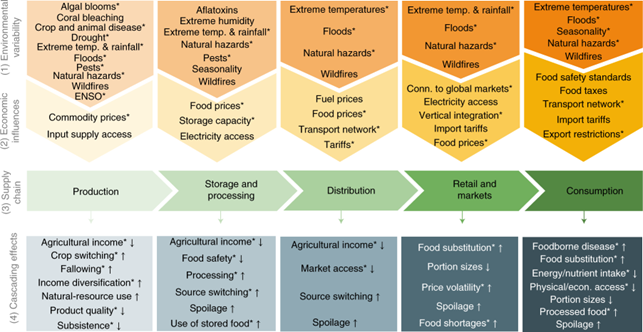
Figure | Entry points for environmental variability in food supply chains. 1) Environmental variability can enter at each step of the food supply chain. 2) Economic conditions and infrastructure quality can dampen or enhance these environmental factors. A variety of geopolitical and other economic factors influencing the interactions of environmental variability and food supply chains are also discussed in the text. 3) The impacts of this variability on food quantity and quality can also be passed between steps in the food supply chain. 4) The cascading effects represent the main outcomes that could occur without intervention from supply chain actors, and the direction of the arrow next to each effect indicates whether there would be an expected increase or decrease. Depending on the specific context, only certain cascading effects may emerge in response to environmental variability. The asterisks indicate a type of environmental variability, economic influence or cascading effect that was identified within the scoping review. Temp., temperature; conn., connectivity; econ., economic.





