June 01, 2023 |Global Food Security | Source |
Introduction: Calls are rising for food system transformation to meet both human and planetary goals. Challenges include reducing greenhouse gas emissions and ensuring food systems are sustainable and equitable. Seaweed is proposed as a solution due to its potential to address food insecurity and mitigate the carbon footprint of food systems. Researchers from Tufts University in US and Wordfish examin seaweed's potential in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) and its environmental benefits.
Key findings: Seaweed production has significantly increased globally, with China being the largest producer. However, Indonesia has emerged as a key player in seaweed farming, particularly for species used in carrageenan production. While seaweed farming presents opportunities for income generation, especially for women in coastal communities, challenges like pathogen outbreaks and climate change impact productivity. Processing and trade of seaweed products contribute to the economy, with Southeast Asia dominating the market. LMICs, like India, are investing in seaweed farming to boost production and create jobs. Yet, consumer acceptance of seaweed in diets remains limited, especially outside of Asia, due to taste preferences and neophobia. Promoting seaweed consumption hinges on highlighting its health benefits, but its integration into local diets in LMICs may require innovative product development rather than direct consumption. Nonetheless, seaweed processing holds potential for income generation and dietary diversity in LMICs, provided supportive policies and market conditions are in place.
The potential of seaweed as a valuable resource in LMICs faces both challenges and opportunities. While seaweed farming holds promise for income generation and nutritional enhancement, it has yet to receive significant attention compared to other forms of aquaculture. Policy support, infrastructure, and investments are needed to expand seaweed production and value addition. Coastal regions in Africa and Asia offer suitable environments for seaweed farming, but data limitations hinder targeted investments. Risks associated with seaweed production include environmental hazards, competition for space, labor constraints, and seed quality issues. However, market-based approaches could facilitate economic growth through seaweed value chains, provided there are investments in processing, packaging, and quality assurance. Addressing food safety concerns and building trust in seaweed products are essential for market success. Improved data collection and research are necessary to unlock the full potential of seaweed farming in LMICs and ensure its contribution to sustainable development goals.
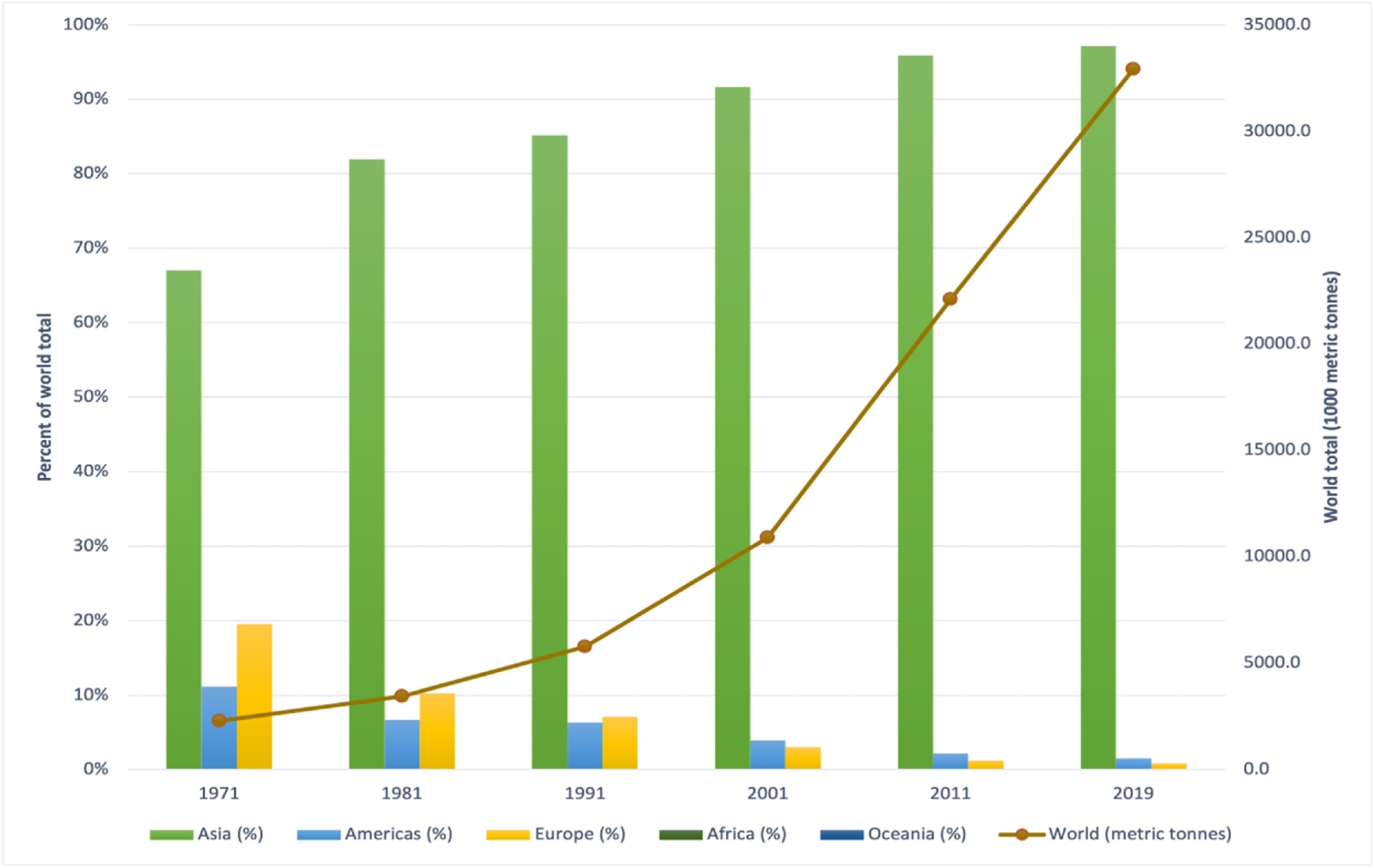
Figure | Global trends in aquatic plant supply, 1971–2019.





