September 29, 2022 | Environmental Research Letters | Source |
Introduction: The food we eat has far-reaching impacts on both the environment and our health. While much of the environmental strain originates from agricultural production, the root causes and solutions are spread across the entire food system, from farm to fork to waste management. In this study, researchers from Chalmers University of Technology and Federation of Swedish farmers focus on understanding and quantifying the nitrogen footprint, which measures the emissions of reactive nitrogen utilizing a comprehensive inventory spanning agricultural production, food processing, waste management, and wastewater treatment.
Key findings: The research finds that the average Swedish food nitrogen footprint is 12.1 kg per capita per year. Surprisingly, a significant portion of this footprint, 38%, arises from food production abroad. Animal products make up the majority of both the nitrogen footprint and protein intake, suggesting room for reduction through dietary shifts. Additionally, a substantial portion of food waste nitrogen is unavoidable, stemming from non-edible parts like bones. Overall, the study provides a detailed method for assessing nitrogen footprints, highlighting opportunities for mitigating environmental impacts through dietary changes and waste reduction. This approach offers valuable insights complementary to traditional environmental indicators, enhancing our understanding of food system sustainability.
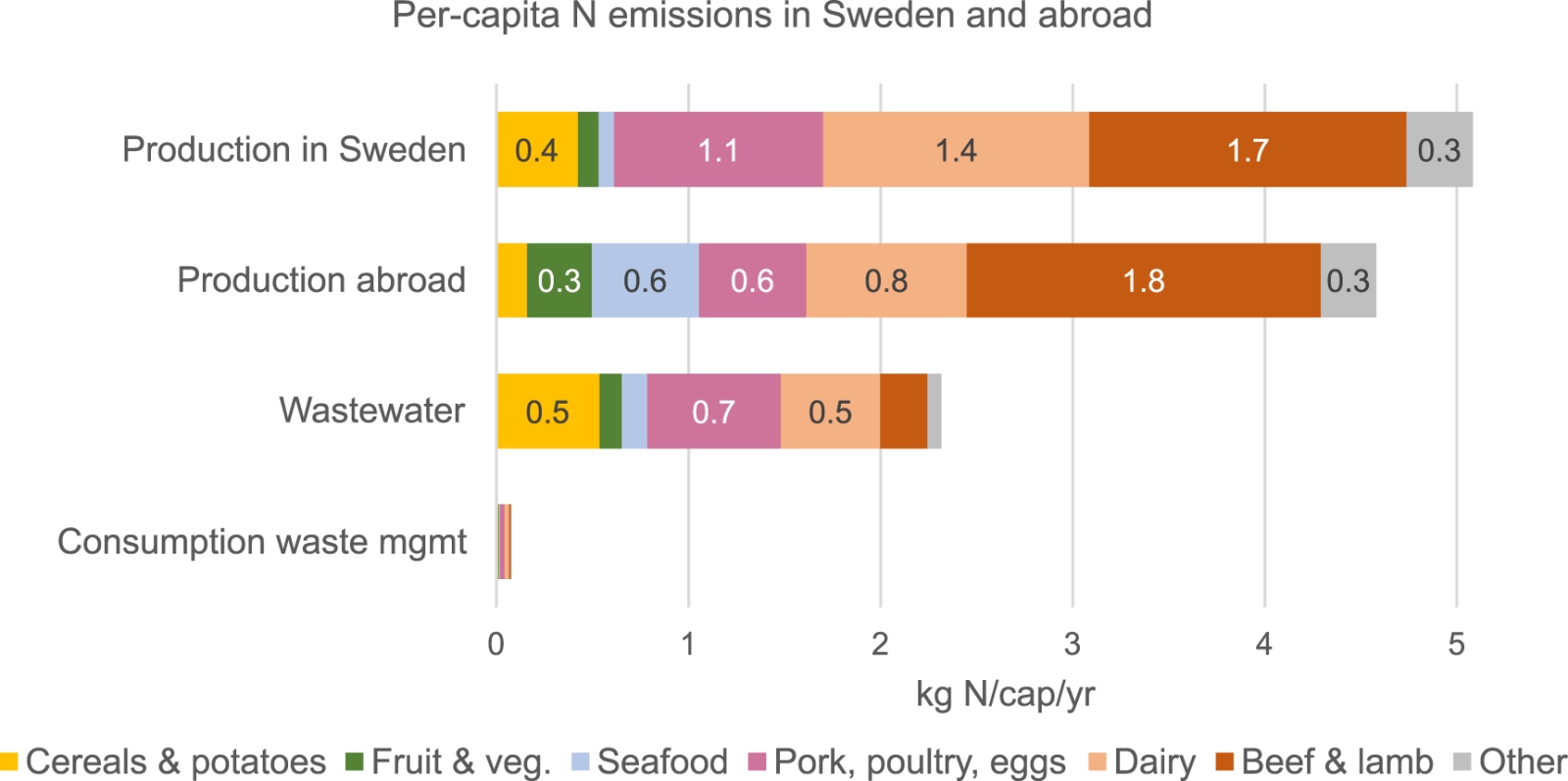
Figure | The food N footprint of the average Swedish consumer (total 12.1 kg N capita−1 yr−1), divided between food products and between different parts of the production and consumption chain. The category other includes margarine and vegetable oils, pulses, offal and game and other meat, sugar, and alcoholic beverages.





