February 10, 2020 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Source |
Introduction: The demand for food due to population growth has led to the industrialization of food production, particularly in sectors like apple juice production. However, this shift has resulted in increased energy consumption, primarily from fossil fuels, leading to environmental risks for both human health and ecosystems. To address this issue, it's crucial to pinpoint the key areas of energy consumption and environmental impact within food production systems to enhance their efficiency and sustainability.A recent study led by University of Tehran in Iran focused on analyzing the energy consumption and environmental impacts of apple juice production in Iran's West Azarbaijan province. Using energy flow and life cycle assessment (LCA) methods, researchers traced the energy usage and greenhouse gas emissions from the farm gate to the packaging of bottled juice.
Key findings: The study revealed that apple juice production consumes approximately 28.33 megajoules of energy per bottle, with diesel fuel, natural gas, and polyethylene terephthalate bottles being major contributors. Moreover, the life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions were estimated at 1.83 kilograms of CO2 equivalent, primarily attributed to diesel and natural gas combustion.
Additionally, the study identified significant environmental impacts, such as acidification and eutrophication, mainly stemming from agricultural practices like fertilizer and pesticide use. Chemical fertilizers and farmyard manure contributed most to acidification and eutrophication, while pesticides were prominent in other impact categories like human toxicity and aquatic ecotoxicity.
The findings suggest potential strategies to mitigate environmental burdens, including the use of bio-fertilizers, biological control methods in agriculture, and the adoption of renewable energy technologies in the juicing process. These measures could help reduce the environmental footprint of apple juice production, promoting sustainability in the food industry.
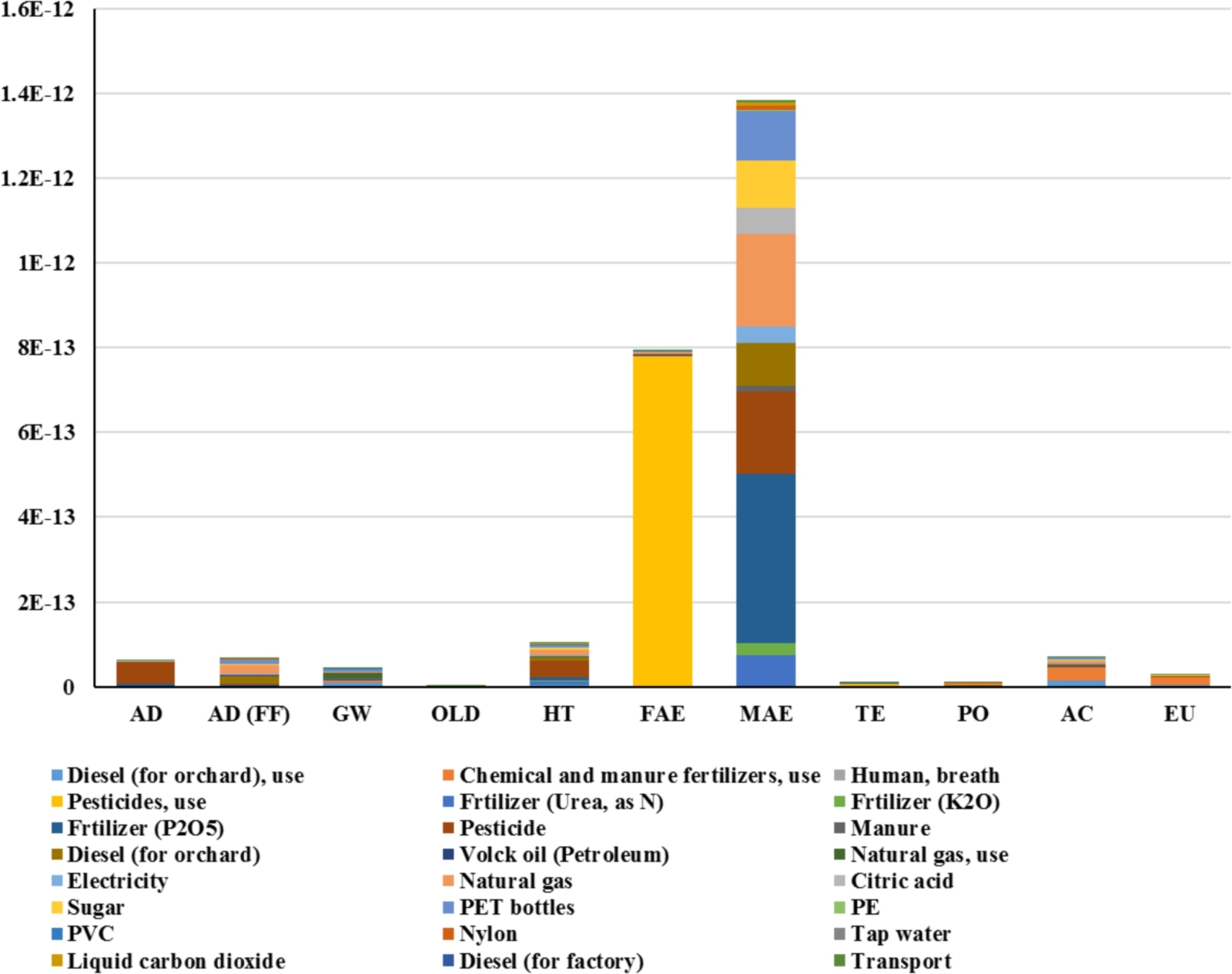
Figure | Contributions of various inputs to the normalized environmental impact categories in the second phase of apple juice production.





