January 17, 2024 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Source |
Introduction: The world's population, increasingly concentrated in urban areas, poses challenges to sustainability and food security. With projections showing a rise to 9.7 billion by 2050 and urbanization reaching 68.4%, sustainable food systems are crucial. Climate change threatens agriculture, highlighting the need for resilient solutions like hydroponics, especially in urban settings. Researchers from the University of Minho, University of Porto, and University of Coimbra in Portugal review the home hydroponic systems that enhance food self-sustainability while reducing environmental impact.
Key findings: Hydroponics, a soil-less farming technique, offers a sustainable and efficient way to grow crops in urban environments. It allows precise control over factors like nutrient concentration and pH levels, resulting in faster growth and higher yields compared to traditional agriculture. Home hydroponic systems, though requiring initial investment and technical knowledge, have the potential to increase food security, promote local economies, and reduce the environmental footprint of food production.
Despite its benefits, challenges such as high initial costs, technical requirements, and potential waterborne disease risks need to be addressed for widespread adoption. However, with advancements in technology and increased awareness, urban agriculture, especially through hydroponics, holds promise for enhancing food self-sufficiency and resilience in urban areas while contributing to environmental sustainability.
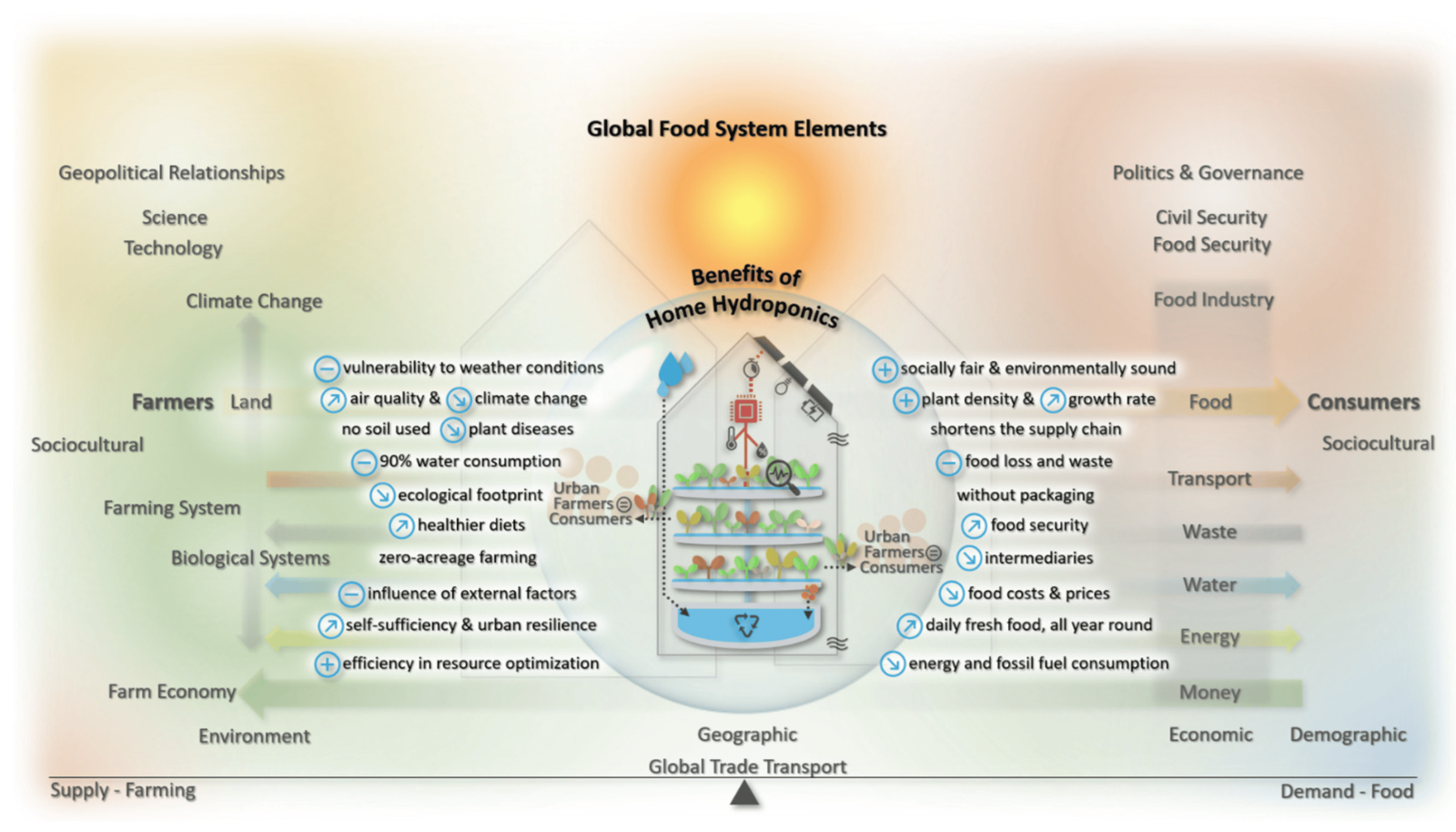
Figure | Conceptual approach to the benefits of home hydroponics in light of the current global food system. The background of the global food system was adapted from ShiftN CVBA.





