Apr 13, 2023 | Frontiers in Environmental Science |
A recent study conducted by Northeast Agricultural University in China explored the impact of digitalization on low-carbon agricultural production in the country. With the rapid advancements in technologies like artificial intelligence, big data, and cloud computing, China's agriculture is entering a new digital era. The researchers analyzed provincial data from 2013 to 2020 and used advanced statistical models to investigate the relationship between digitalization and agricultural carbon emissions, considering resource misallocation.
The results showed that digitalization plays a significant role in curbing carbon emissions in agriculture, thus promoting low-carbon agricultural production. This effect remained consistent even after conducting robustness tests to ensure the reliability of the findings. Interestingly, the study found that the impact of digitalization on reducing carbon emissions was most pronounced in the eastern region of China compared to the central and western regions.
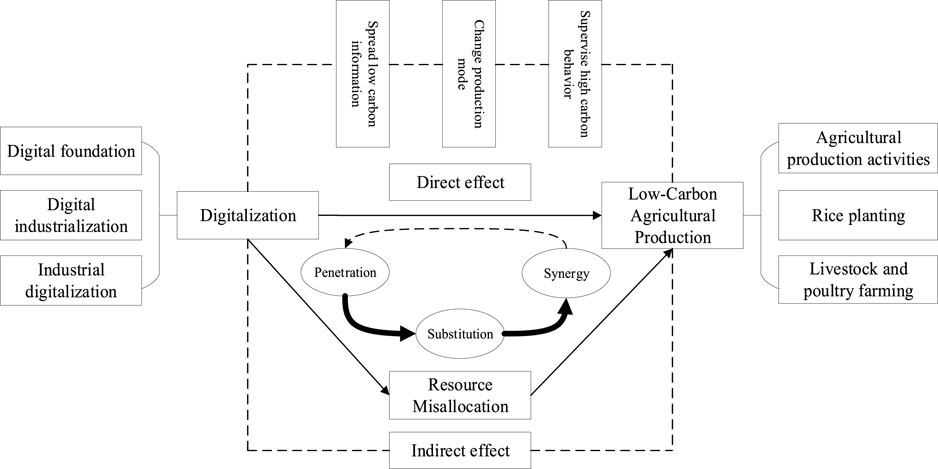
Furthermore, the researchers conducted a mechanism analysis, which revealed that digitalization helps rectify the widespread misallocation of capital and labor in agricultural factor markets. These findings hold significant policy implications for promoting low-carbon agricultural practices in China, highlighting the potential of digital technologies to contribute to a more sustainable agricultural sector.
The impact mechanism of digitalization on low-carbon agricultural production