February 24, 2022 | Nature Food |
Introduction: The study highlights the importance of considering agriculture and land use in climate change mitigation efforts alongside the energy sector. A global research team led by researchers based in Kyoto University and Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences examined how policies like bioenergy crop expansion, emissions reduction in agriculture, and afforestation impact food security. By analyzing various scenarios, the research provides insights crucial for designing effective policies that reduce emissions without compromising food security.
Key findings: The findings reveal that afforestation, often induced by carbon pricing, could significantly affect food security compared to non-CO2 emissions policies. Approximately 41.9 million and 26.7 million additional people could be at risk of hunger in 2050 due to these measures, highlighting the need for better coordination in emissions reduction policies. The study underscores the complexity of addressing food security concerns within climate change mitigation efforts and suggests the importance of holistic approaches. It also emphasizes the role of technological advancements, policy interventions, and demand-side transitions in mitigating adverse impacts on food security while achieving emissions reduction goals.
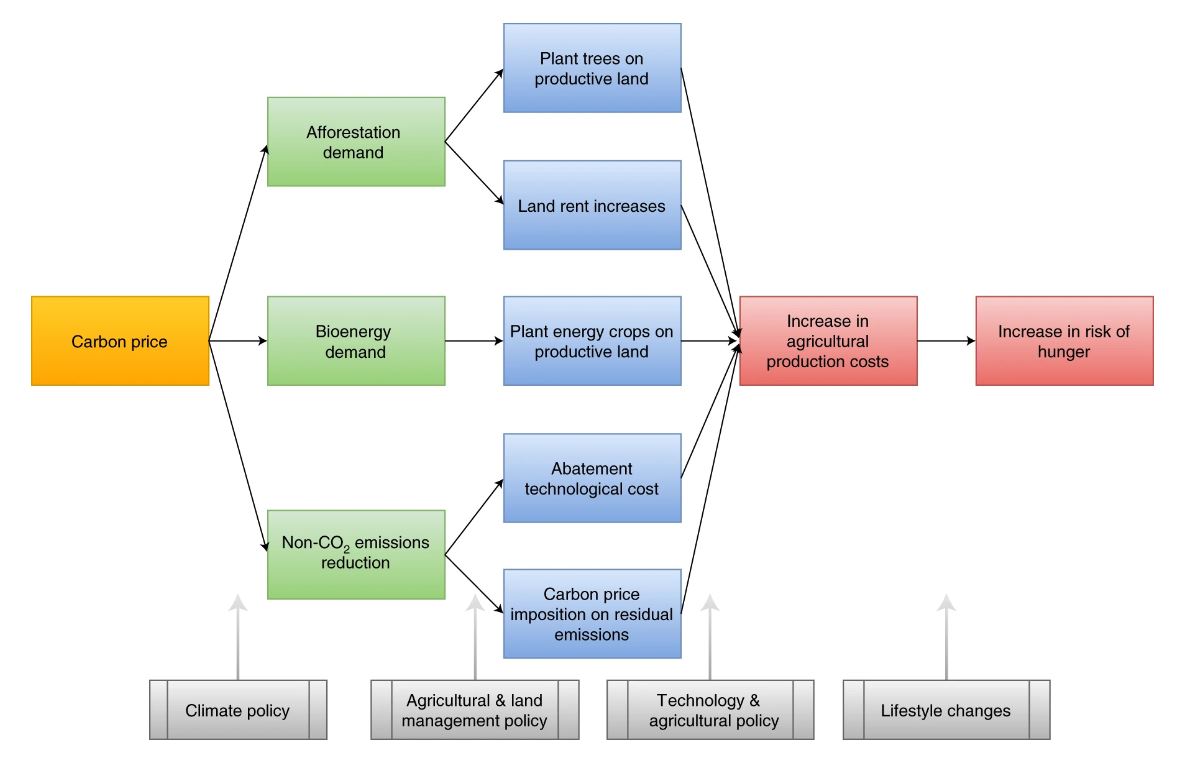
Figure | Representation of climate change mitigation measures and their potential effects on agricultural prices and the risk of hunger. The three measures considered—namely afforestation, bioenergy and non-CO2 emissions reduction—are shown in the green boxes and can be decomposed into secondary factors (blue boxes). These can affect agricultural production costs, which in turn might affect food security. Sectoral policies and lifestyle changes (grey arrows at the bottom) can be targeted at different elements of the figure.