February 09, 2024 | Scientific Reports |
Introduction: On May 7, 2022, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and National Development and Reform Commission of People's Republic of China proposed to increase the carbon sequestration capacity of agricultural land under the “Agricultural Rural Carbon Emission Reduction Program.” Researchers from the College of Economics and Management in China assess the potential of farmland improvements, such as leveling of land and construction of irrigation system in reducing GHG emission reduction and increasing carbon sequestration.
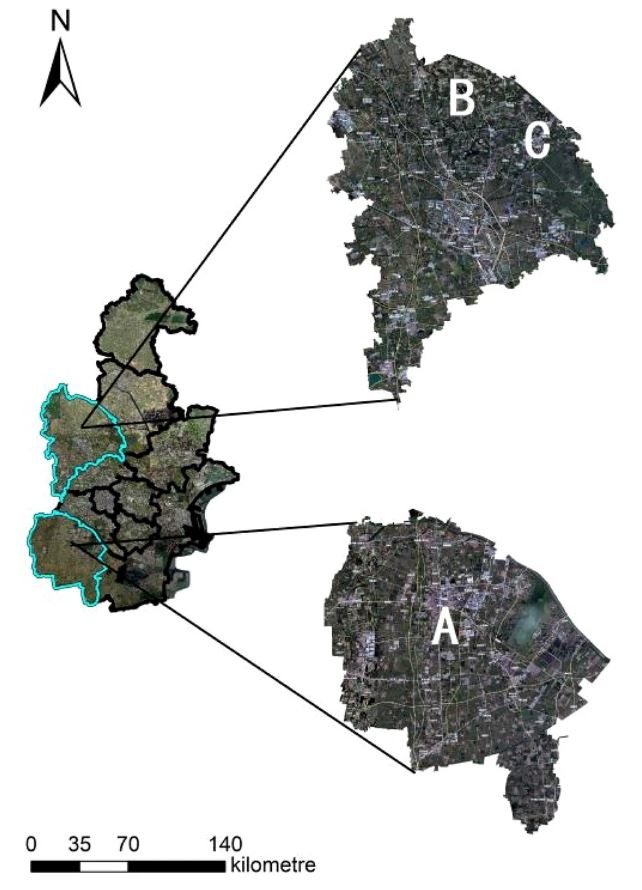
Key findings: The research team applied whole life cycle theory in construction projects to planning and completion of earthworks for improving farmland, and caculated net carbon effects of farmland improvement. For the case studies of Tianjin, China, the researchers have quantified and analyzed emissions from materials and energy consumption during construction phase, as well as changes in carbon sequestration during farmland operation. While carbon emissions may temporarily increase during earthworks, the net impact on the environment will become carbon negative after project completion.
Efforts should focus on reducing energy consumption during construction phase, scientifically optimizing project scales and landscape design to enhance carbon sequestration capacity. By integrating ecological considerations into farmland improvement and management practices, it's possible to mitigate the environmental impact of agriculture and reduce carbon emission.
Figure | Schematic of the project area