Comparing the carbon footprints of urban and conventional agriculture
January 22, 2024 | Nature Cities |
Introduction: Urban agriculture (UA) is seen as a key solution for creating sustainable urban food systems. In collaboration with European researchers, a US research team based in University of Michigan compared the environmental impact of UA to conventional agriculture across 73 sites in Europe and the United States.
Key findings: Results showed that UA produces six times more carbon emissions per serving compared to conventional farming. However, some UA crops and sites outperform conventional agriculture, suggesting ways to reduce climate impact. Recommendations include cultivating crops typically grown in greenhouses or air-freighted, prolonging UA infrastructure lifespan, and utilizing urban waste for inputs. Despite UA's higher carbon intensity, it offers social benefits like improved mental health and community building. Future research should explore strategies to mitigate UA's environmental impact while maximizing its social and nutritional benefits.
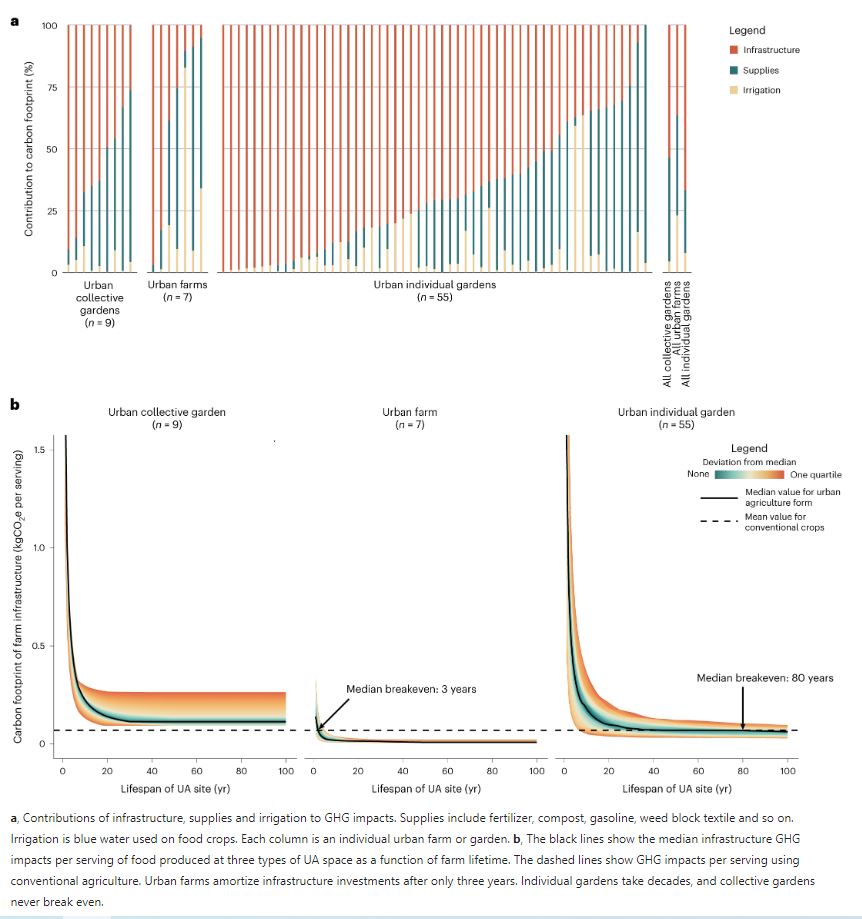
Figure | Infrastructure and carbon footprints at urban agriculture sites.
Viewed Articles
January 22, 2024 | Nature Cities |Introduction: Urban agriculture (UA) is seen as a key solution for creating sustainable urban food systems. In collaboration with European researchers, a US research
Read More
October, 2023 | Agricultural Systems | Source | Introduction: Ireland’s beef sector, responsible for 37% of national greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, presents key opportunities for climate mitigation
December 15, 2023 | Journal of Environmental Management | Source | Introduction: Livestock production is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions (GHGE) in China, challenging the country’s 20
October 15, 2021 | Fuel | Source | Introduction: A research team from SRM Institute of Science and Technology and Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering in India reviews sustainable pathways
February 28, 2024 | Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment | Source | Introduction: Despite existing mitigation efforts, integrated approaches addressing system-wide emissions—including soil organic c
June 24, 2024 | Humanities and Social Sciences Communications | Introduction: Digital inclusive finance is widely promoted as an enabler of green transitions, yet its environmental impacts in agricul





