Precision Agriculture | Mar 7, 2023
Researchers from the University of Prince Edward Island in Canada have developed an innovative and cost-effective protocol for monitoring plant health in agricultural fields using high-resolution multispectral imaging. By leveraging machine vision (MV) and generative adversarial networks (GAN), they were able to convert standard red-green-blue (RGB) imagery captured by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) into valuable normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) maps.
Traditionally, NDVI maps were generated from near-infrared (NIR) imagery, but this study directly translated RGB imagery into NDVI, making it more accessible and affordable. The researchers tested the protocol using a fixed-wing UAV equipped with a RedEdge-MX sensor to capture images from different potato fields throughout the 2021 growing season.
By training and evaluating GAN models, particularly Pix2Pix and Pix2PixHD, they found that Pix2PixHD outperformed Pix2Pix in terms of accuracy and performance. The protocol demonstrated breakthrough results, enabling cost-effective monitoring of vegetation and orchard health. The trained GANs can generate useful vegetation index maps for precision agriculture practices, including variable rate applications. Additionally, the protocol has the potential to analyze remote sensing imagery of large-scale agricultural fields and commercial orchards, extracting essential information about plant health indicators.
This study presents an exciting advancement in economically monitoring plant health and offers valuable insights for precision agriculture and remote sensing applications.
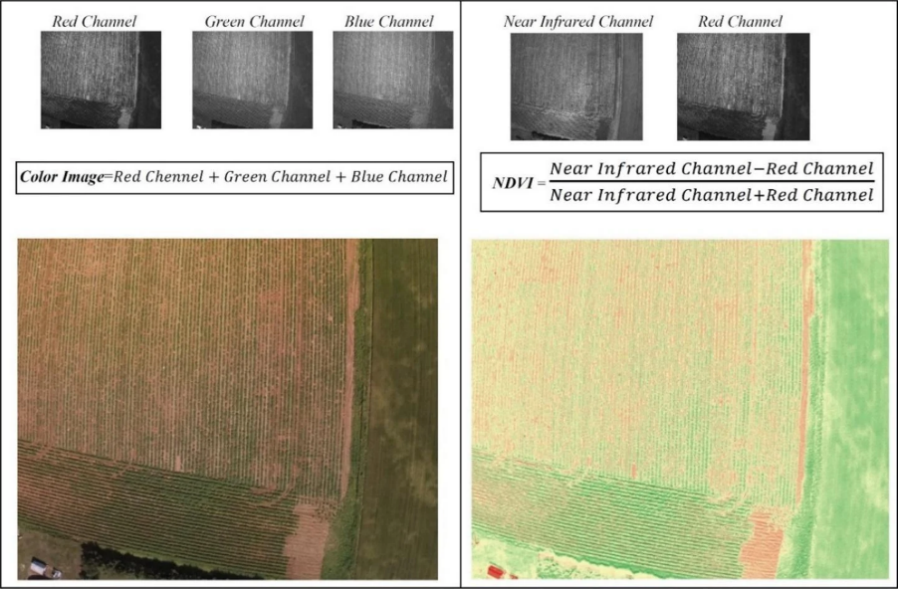
Generated dataset sample for the training of generative adversarial networks used in the design of the proposed protocol. The left image represents the input image which is the combination of the red, green, and blue channels, while the target image is the NDVI image which is the computation index of the red and near-infrared channels.





