August 18, 2022 | Nature Climate Change | Source |
Introduction: An international research consortium led by researchers from Chinese Academy of Sciences evaluates the climate chanage mitigation effects of Natural Climate Solutions (NCS) in China, quantifying the historical and projected mitigation capacity of forest and wetland conservations.
Key findings: Historical data suggests that Natural Climate Solutions (NCS) in China mitigated around 8% of fossil CO2 emissions from 2000 to 2020. Looking ahead, projections indicate that new NCS activities could potentially offset 6% to 8% of fossil CO2 emissions during 2020–2030 and 2020–2060, with costs ranging from US$10 to US$100 per MgCO2e. However, NCS alone cannot solve climate issues; urgent priorities include energy transformation and low-carbon technology adoption. Multilevel governance strategies are essential for maximizing the synergies among various NCS pathways and achieving climate mitigation goals while ensuring ecosystem service co-benefits. Challenges include uncertainties due to climate and ecosystem shifts, limited data availability, and the need to consider co-benefits and socioeconomic factors in NCS planning and implementation.
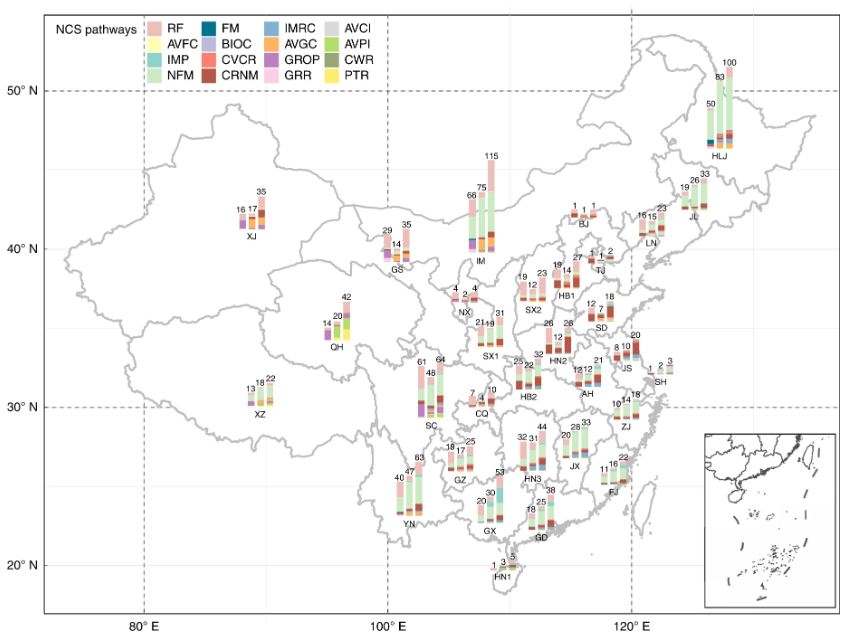
Figure | Historical mitigation capacity and future NCS potential by each NCS pathway across the provinces of China. The numbers above each of the three bars for each province represent the total flux (TgCO2e yr−1) in the periods of 2000–2020, 2020–2030 and 2020–2060, respectively. AH, Anhui; BJ, Beijing; CQ, Chongqing; FJ, Fujian: GD, Guangdong; GS, Gansu; GX, Guangxi; GZ, Guizhou; HB1, Hebei; HB2, Hubei; HLJ, Heilongjiang; HN1, Hainan; HN2, Henan; HN3, Hunan; IM, Inner Mongolia; JL, Jilin; JS, Jiangsu; JX, Jiangxi; LN, Liaoning; NX, Ningxia; QH, Qinghai; SC, Sichuan; SD, Shandong; SH, Shanghai; SX1, Shaanxi; SX2, Shanxi; TJ, Tianjin; XJ, Xinjiang; XZ, Xizang; YN, Yunnan; ZJ, Zhejiang.