April 21, 2023 | Science | Source |
Introduction: Humanity is facing severe social and ecological impacts due to climate change and biodiversity loss, which are deeply interconnected. Based on extensive literature review, a global research consortium led by Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Researc in Germany proposed strategies to overcome the coupled climate and biodiversity crisis.
Key findings: Both crises are driven by human activities, such as greenhouse gas emissions and habitat destruction, and they exacerbate each other’s effects. This leads to rising temperatures, extreme weather, and loss of species, which harm ecosystems and human well-being. To tackle these issues, drastic reductions in greenhouse gas emissions are essential. Protecting and restoring natural environments, like forests and oceans, can help capture and store carbon, while also supporting biodiversity. Policies ensuring fair access to natural resources are crucial for sustaining human well-being. Key strategies proposed include:
- Reducing emissions and adapting to climate changes.
- Protecting 30-50% of land, ocean, and freshwater areas.
- Promoting sustainable development that avoids overconsumption and waste.
- Ensuring equitable access to natural resources for all.
Coordinated global efforts are needed to achieve these goals and create a sustainable future. Without significant and immediate action, current and future targets for biodiversity and climate will not be met, leading to increased human vulnerability and ecological degradation. Transformative changes in policies and behaviors are necessary to secure a healthy planet for future generations.
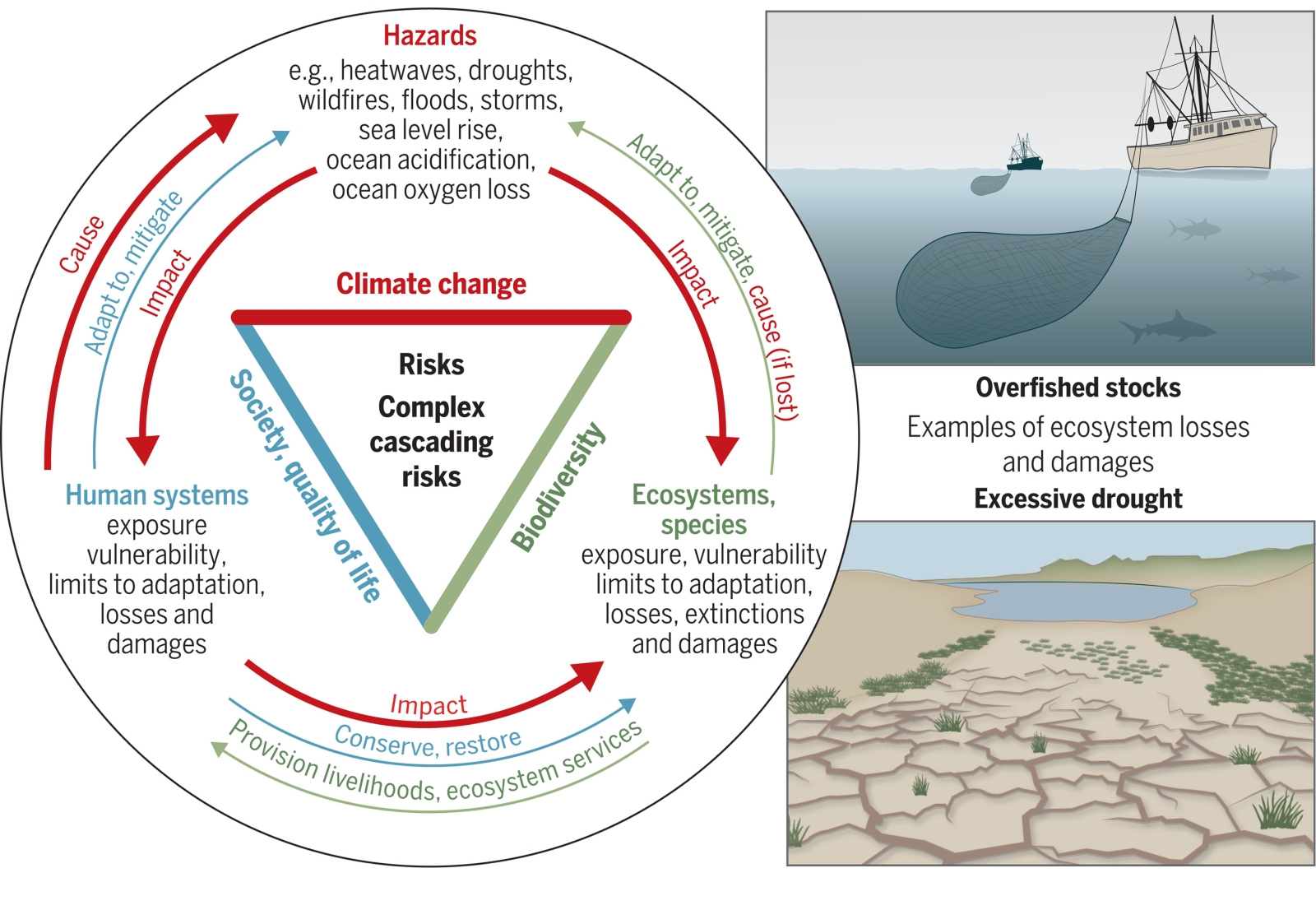
Figure | Climate, biodiversity, and human society are coupled through dynamic interactions across scales. Human-caused exploitation and climate change are increasingly threatening biodiversity and nature’s contributions to people, causing losses and damages exemplified through overfished stocks and excessive drought that harm productive habitats.





