January 20, 2024 | Scientific Reports | Source |
Introduction: Conventional farming practices requires high energy inputs, such as in the production and transportation of mineral nitrogen fertilizers. A German research team based in Technical University of Munich examines current technologies for reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions through innovations like precision farming and renewable energy integration, as well as compare the organic (OF) and conventional farming (CF) in terms of energy efficiency.
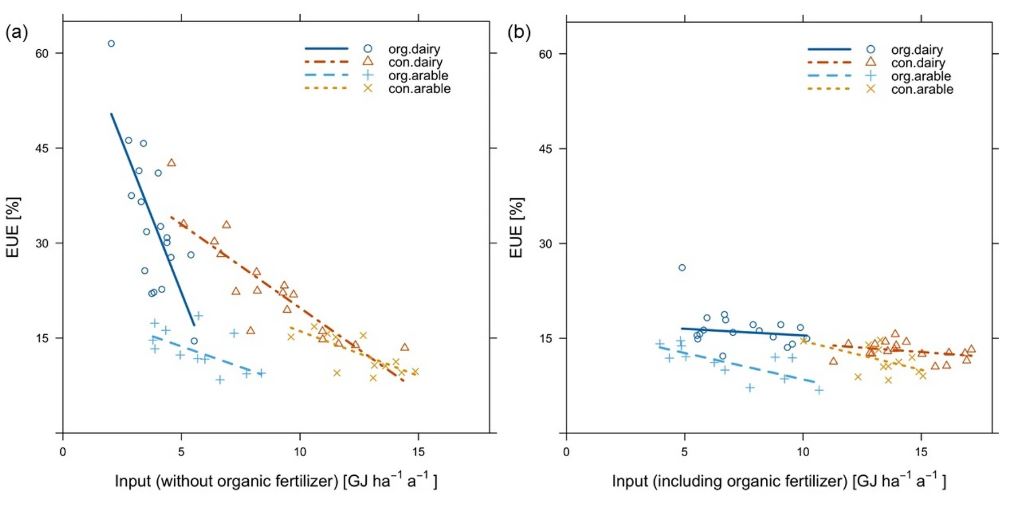
Key findings: The results of analyzing energy input, output, and efficiency (EUE) across 30 pairs of arable and dairy farms show substantial heterogeneity between systems and individual farms, influenced by factors like crop rotation, fertilization intensity, and farm structure. OF generally exhibited lower energy input and output compared to CF, with higher EUE observed in dairy farming. Strategies to close the yield gap between OF and CF include plant breeding and optimizing crop rotations. Increasing EUE involves reducing fossil energy inputs and enhancing energy retention through renewable energy use and efficient technologies. Urgent reductions in fossil energy use are needed to mitigate climate change and reduce dependence. Comparing energy flux efficiency among farming systems offers insights into sustainable resource use.
Figure | Farming system-specific relationship between energy input and EUE (a) without organic fertilizers and (b) including organic fertilizer.