June 20, 2022 | Nature Food | Source |
Introduction: Global food trade doubled since 1995, reaching $1.5 trillion in 2018, crucial for food security. "Food-miles" measure environmental impact, but comprehensive carbon footprint assessments are lacking. Highlighting the need for integrated food security and environmental strategies, researchers from the University of Sydney in Australia and from Wuhan University in China propose a method to integrate food-miles emissions, food production and land-use change emissions in the calculation of carbon footprint.
Key findings: It is estimated that food-miles, the distance food travels from production to consumption, contribute substantially to greenhouse gas emissions, comprising about 19% of total emissions from the food system. Surprisingly, the emissions from transporting vegetables and fruits alone surpass those from their production, indicating a heavy environmental cost associated with their transportation. To reduce emission of food-systems, there is a growing call to shift towards plant-based diets and promote locally produced food items, especially for wealthier nations to reduce the reliance on food that need to be transported long-distance. By understanding and addressing the emissions associated with food transportation, it's possible to make more informed decisions about food production and consumption, ultimately mitigating the environmental impact of the global food system.
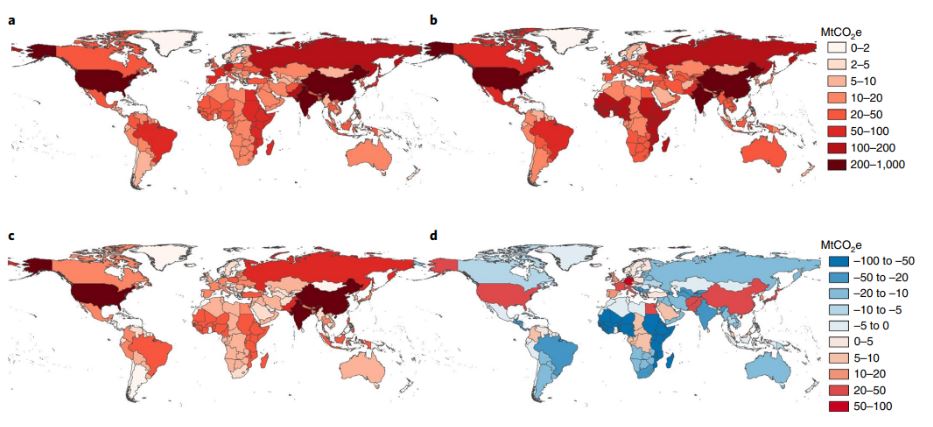
Figure | Global food-miles emissions broken down by countries/regions. a, Destination-based food-miles emissions. b, Origin-based food-miles emissions. c, Domestic food-miles emissions. d, Food-miles emissions net trade. Destination-based (a) and origin-based (b) food-miles emissions (Supplementary Notes and Supplementary Methods, equations (9)–(12)) are obtained by summing the food-miles emissions of supply chains flowing into and out of a region. Domestic food-miles emissions (c) refers to supply chains providing domestic production and consumption. Food-miles emissions net trade (d) is given by the difference between destination and origin, which is <0 for net food-miles emissions importers and >0 for net food-miles emissions exporters.