May 07, 2024 | Nature Communications | Source |
Introduction: Providing sustainably produced food while safeguarding ecosystem services is a global challenge. Researchers from Institute of Agricultural Sciences in Switzerland investigate the effectiveness of three grassland management practices—organic production, extensive management, and harvest type—on enhancing ecosystem-service multifunctionality by analyzing 22 indicators across 86 grasslands in Switzerland.
Key findings: The findings reveal that while organic farming has limited impact, Eco-scheme and harvest type significantly influence ecosystem services. Eco-scheme, which prohibits fertilization, improves cultural services but reduces provisioning services like biomass yield. Similarly, pastures enhance cultural services but may trade-off with some provisioning services. The positive effects of Eco-scheme and pasture are mainly due to reduced land-use intensity, such as lower fertilizer input and less frequent harvesting.
Ultimately, the study suggests that diversifying grassland management across landscapes can improve ecosystem-service multifunctionality, meeting various societal needs. Combining these management practices strategically can optimize the provision of services that are in short supply, supporting more sustainable and resilient agricultural systems.
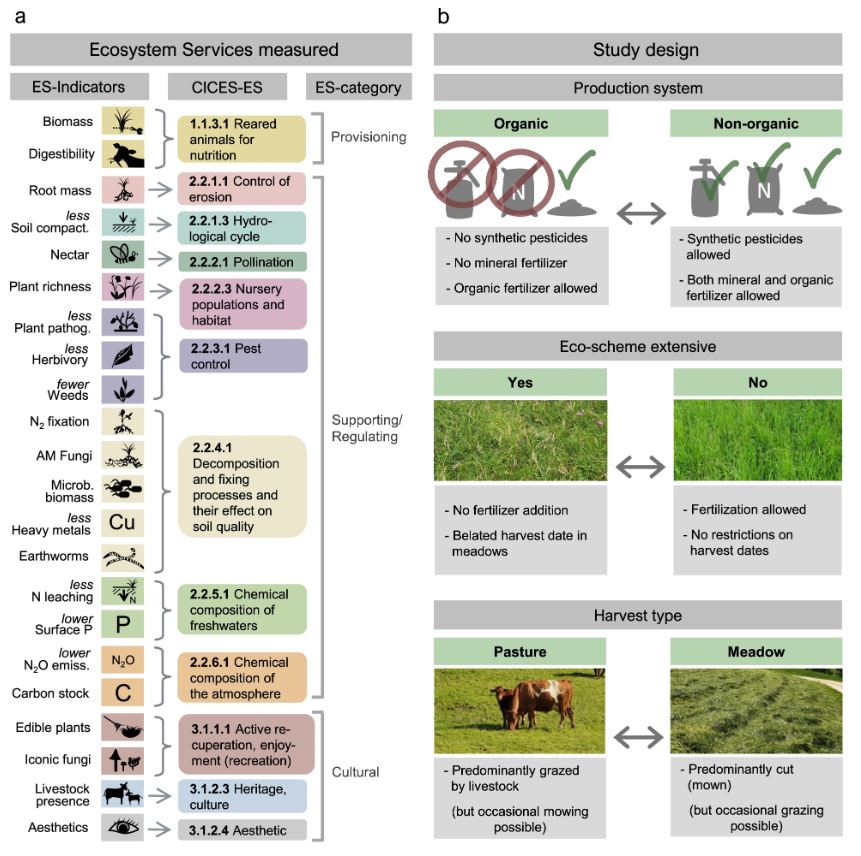
Figure | Overview of measured ecosystem-service indicators (ES-indicators) and study design. a From left to right: indicators grouped according to the corre-sponding ecosystem service deÔ¨Āned by CICES29 and corresponding ecosystem-service category. b From top to bottom: brief deÔ¨Ānition of the three management aspects studied: Production system, Eco-scheme, and Harvest type. All 22 ecosystem service indicators were measured for the eight possiblec ombinations of Production system, Eco-scheme, and Harvest type. Total number of study plots was 86.