February 09, 2023 | Nature Food | Source |
Introduction: Researchers from University of Cambridge, UK examine the global impact of synthetic nitrogen fertilizers and manure on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across their entire life cycles.
Key findings: By analyzing data from 2019, the study highlights that current fertilization practices emit significant amounts of GHGs, with synthetic fertilizers alone responsible for approximately 1.31 gigatons of CO2-equivalent emissions annually. A substantial portion of these emissions occurs during the use of fertilizers in agricultural fields, primarily due to the release of nitrous oxide (N2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Key strategies identified to mitigate these emissions include enhancing nitrogen-use efficiency in crop production and decarbonizing the production processes of fertilizers. Proposed interventions, such as using nitrification inhibitors to reduce N2O emissions and shifting to more efficient fertilizer types, could collectively reduce global emissions by up to 84% by 2050.
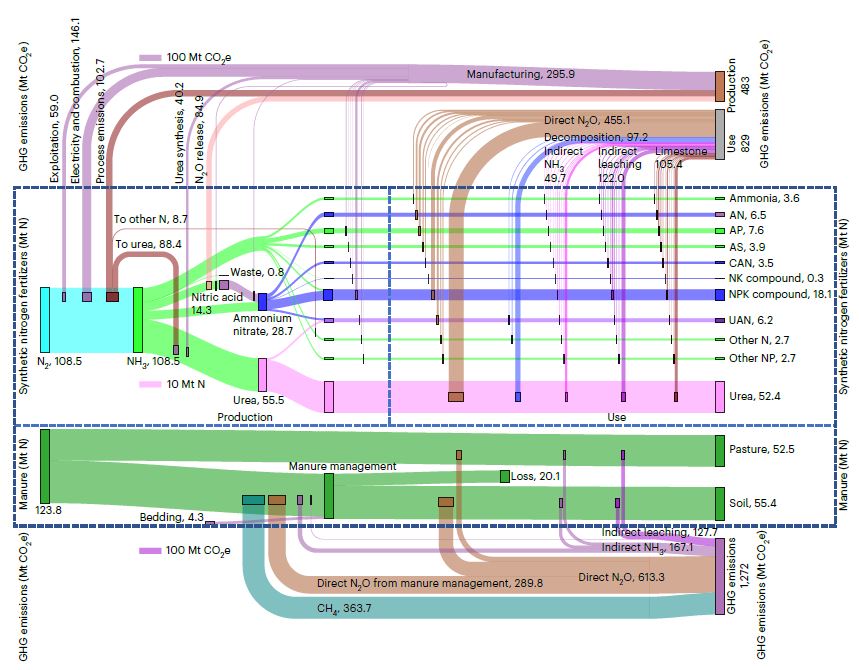
Figure | Sankey diagram of the global mass flow of synthesized nitrogen fertilizers and manure and corresponding GHG emissions in each life-cycle stage in 2019. The horizontal flows represent the mass flows of nitrogen, and the vertical flows show the points of generation of GHG along the supply chain. In both cases, the thickness of the line is proportional to the mass of nitrogen and GHG emissions, respectively. The mass of nitrogen fertilizers flows from left to right along its supply chain. AN, ammonium nitrate; AP, ammonium phosphate; AS, ammonium sulfate; CAN, calcium ammonium nitrate; NK, nitrogen potassium; NPK, nitrogen phosphorus potassium; UAN, urea ammonium nitrate; N, nitrogen; NP, nitrogen phosphorus.