January 02, 2024 | Communications Earth & Environment | Source |
Introduction: Research team based in Zhejiang University in China applies advanced modeling and machine learning to optimize farming practices in China's North China Plain, balancing high crop yields with reduced greenhouse gas emissions, considering factors like nitrogen use, irrigation, and crop residue management under current and future climate conditions.
Key findings: Current farming practices, including local farmers' methods and trial-based recommendations, often exceed the optimal levels of water and fertilizer input. There is substantial potential for reducing resource inputs like fertilizer and irrigation water by 16% to 20% across the region, while also cutting greenhouse gas emissions. The optimized practices align with achieving maximum crop yields and minimizing environmental impact, crucial in a changing climate scenario. The soil organic carbon sequestration rates over time will decline yet management practices to local situations is needed to sustain agricultural productivity and mitigate climate-related risks.
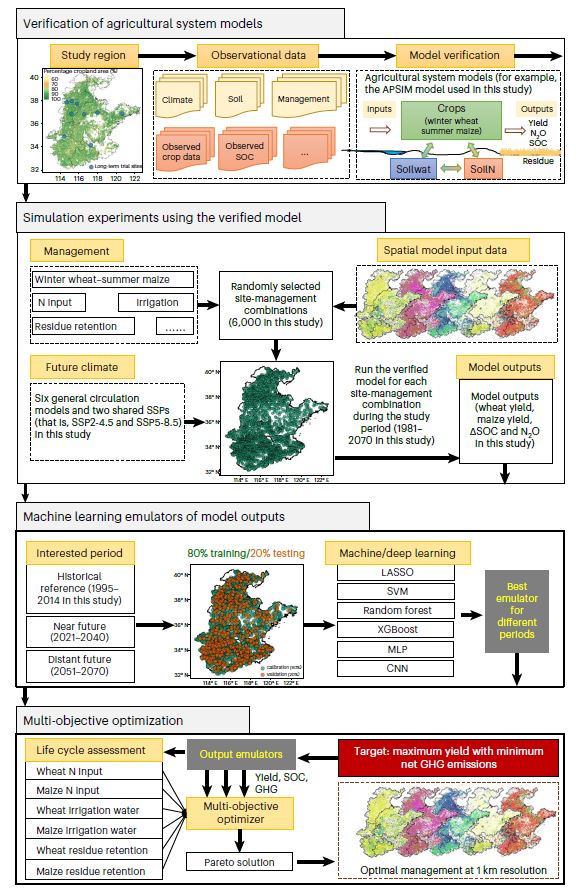
Figure | A simulation framework enables spatiotemporal optimization of multiple management practices. The framework combines verification of biophysical models, machine learning, life cycle assessment and multi-objective optimization to derive the best management combination across space and over time under targets of interests.