May 13, 2024 | Agriculture | Source |
Introduction: Rice is a vital food crop, but its sustainability is threatened by excessive chemical use and monoculture practices. Crop rotation and the use of the beneficial bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris (R. palustris) can enhance soil health and rice yields. Researchers from National Pingtung University of Science and Technology in Taiwan explore the combined effects of crop rotation and R. palustris on rice growth, aiming to develop sustainable farming practices for better productivity and environmental health.
Key findings: Beneficial microorganisms like Purple Non-Sulfur Bacteria (PNSB) increased 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) levels in plants, enhancing photosynthesis. Combining PNSB with crop rotation significantly improved soil fertility, resulting in notable increases in tiller numbers (163%), leaf chlorophyll content (13%), and lodging resistance (66%) compared to untreated plants. This combined treatment also boosted productive tillers per hill (112%), average grain per hill (65%), and grain fertility (26%), leading to a 65% increase in grain yield and a 15% rise in shoot dry weight.
Additionally, PNSB treatment improved soil nutrient levels, including essential elements like phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and iron, further enhancing plant growth. Overall, the incorporation of PNSB in crop rotation strategies can significantly improve rice growth and yield, offering a sustainable approach to addressing global food security and climate change challenges.
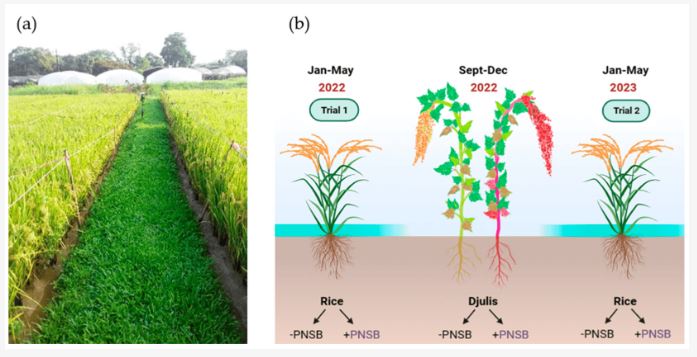
Figure | Enhancement of rice growth and yield through incorporation of purple non-sulfur bacteria (PNSB) in rice-djulis rotation practice. (a) Depiction of the rice fields utilized in this study, where djulis was cultivated as a rotational crop within the same field and (b) a schematic representation of the experimental design implemented in this study.