April 10, 2023 | Nature Communications | Source |
Introduction: Researchers from US and China quantify the global impact of irrigation on energy use and carbon emissions, and provide a roadmap for policymakers and agricultural stakeholders.
Key findings: Annually, irrigation activities account for 216 million metric tons of CO2 emissions and consume 1,896 petajoules of energy worldwide. Surprisingly, despite groundwater sources serving only 40% of irrigated land, they drive a staggering 89% of total irrigation energy use due to the prevalence of energy-intensive diesel pumps. Energy consumption and CO2 emissions can potentially reduced by 90% with more efficient and low-carbon irrigation practices, though careful consideration of regional feasibility and technological advancements is needed.
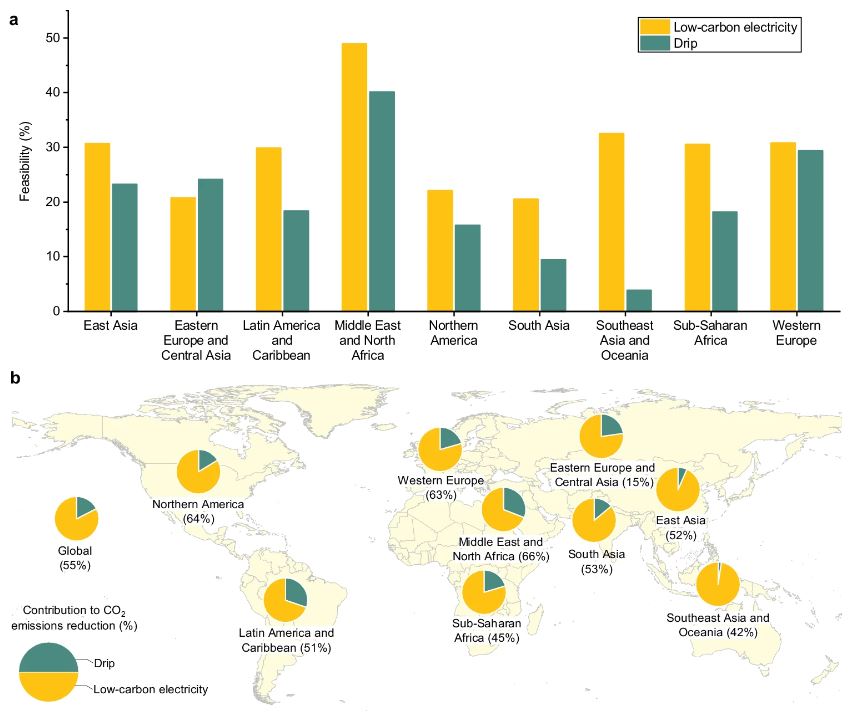
Figure | Feasibility of solutions to reduce CO2 emissions of irrigation on a country-level scale. a Feasibility (%) of drip and low-carbon electricity. b Potential contribution (%) of drip and low-carbon electricity to energy-related CO2 emissions reduction based on the feasibility analysis. The pie chart shows the contribution ratio of low-carbon electricity and drip to energy-related CO2 emissions reduction. The values at the bottom of the pie chart represent the total contribution due to a combination of the two solutions. For a more detailed comparison of regional differences, we further divided the six continents into nine sub-regions (See Source Data for the rationale of the classification)