May 04, 2023 | npj Climate Action |
Introduction: The Paris Agreement aims to limit global temperature rise. Mitigating climate change has economic costs, often measured as a percentage of GDP. Researchers from Kyoto University, Hokkaido University and National Institute for Environmental Studies in Japan explore scenarios, including energy efficiency, renewable energy, sustainable food, and capital formation, to reduce or eliminate these costs. The analysis considers global cumulative GDP loss, emphasizing the need for strategies that don't hinder economic growth. The study also compares mitigation costs with air pollution and climate change damage costs, recognizing the broader societal impacts.
Key Findings: Mitigation costs, projected to range from 1 to 7% of GDP per year, are inversely correlated with the carbon budget, reaching net-zero CO2 emissions around 2050–2070. Socioeconomic-technological transition measures, when fully implemented, can significantly reduce or even make mitigation costs negative, especially with larger carbon budgets. Different measures, such as Additional-Investment, Energy-Supply-Change, Energy-Demand-Change, and Food-System-Transformation, contribute to varying degrees in GDP loss reduction. Renewable energy cost reductions play a limited role, particularly in the long term. The mechanisms behind mitigation cost decrease involve increased capital stock, cost reductions in electricity generation, decreased demand for fossil fuels, and transformations in the food system. Regional implications vary, with reforming regions benefiting more from energy system improvements, and the Middle East and Africa seeing substantial impacts from food system transformations.
Read more: Climate change mitigation costs reduction caused by socioeconomic-technological transitions
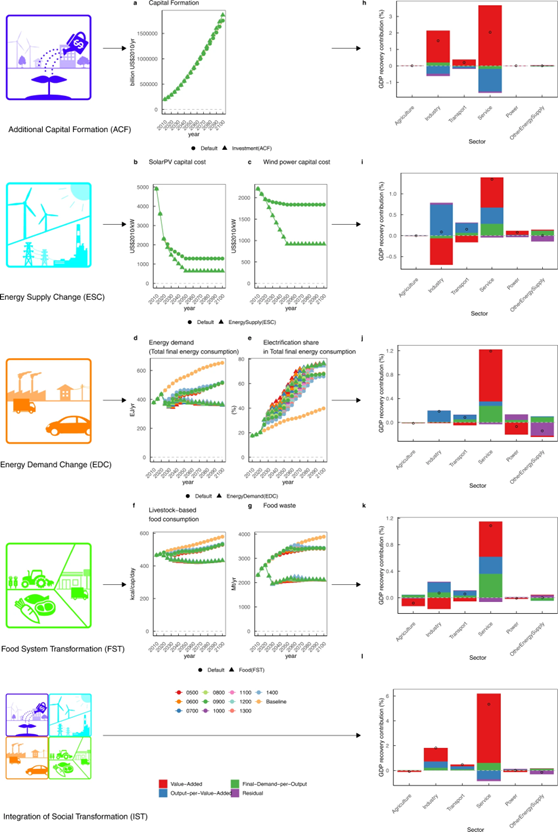
Fig. 2: Mechanism of GDP loss reduction associated with socioeconomic-technological transition and decomposition analysis of GDP loss reduction from the default to socioeconomic-technological transition scenarios under a 1000-Gt CO2 budget for 2100.
Global capital stock, capital cost of solar photovoltaic (PV) and wind turbine technologies, final energy consumption and electrification rates, livestock-based food consumption and food waste generation under various socioeconomic-technological transition scenarios with a 1000-Gt CO2 budget (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, respectively). h, i, j, k, l Shows decomposition analyses of GDP loss reduction by sector. The black circles indicate the total net impacts on GDP loss reduction by sector. All values are expressed in terms of % of overall GDP with different y-axis ranges.





