June 29, 2023 | Nature Communications
Researchers from CIRAD in France conducted a comprehensive study examining the effects of human activities on soil organic carbon (SOC), a crucial component of the Earth's ecosystems with profound implications for climate regulation. In the Anthropocene, an era characterized by significant human influence on the environment, understanding how SOC is influenced by factors such as land use, land management, and climate change is of paramount importance.
To gain deeper insights, the researchers performed a meticulous review, encompassing an impressive 230 first-order meta-analyses that collectively analyzed over 25,000 primary studies. Their second-order meta-analysis synthesized these findings, revealing several critical observations:
- Conversion of natural landscapes into crop fields often results in substantial losses of SOC. However, hope lies in effective land management practices, especially the integration of trees and the incorporation of exogenous carbon sources like biochar or organic amendments, which can partially restore SOC levels.
- In the context of forested environments, certain land management practices may lead to SOC depletion, underscoring the need for careful management strategies to maintain carbon stocks in these ecosystems.
- Surprisingly, indirect effects of climate change, such as those mediated through events like wildfires, have a more pronounced impact on SOC than the direct consequences of rising temperatures.
The findings of this study offer robust evidence to guide decision-makers in preserving SOC reservoirs and promoting land management practices aimed at SOC restoration. Additionally, this research serves as an invaluable roadmap for future investigations, pinpointing specific areas in need of further exploration to bridge existing knowledge gaps regarding the drivers of SOC dynamics. In essence, it provides a scientifically grounded blueprint for safeguarding an often-overlooked but critical component of our planet's environmental stability.
Read more: A global meta-analysis of soil organic carbon in the Anthropocene
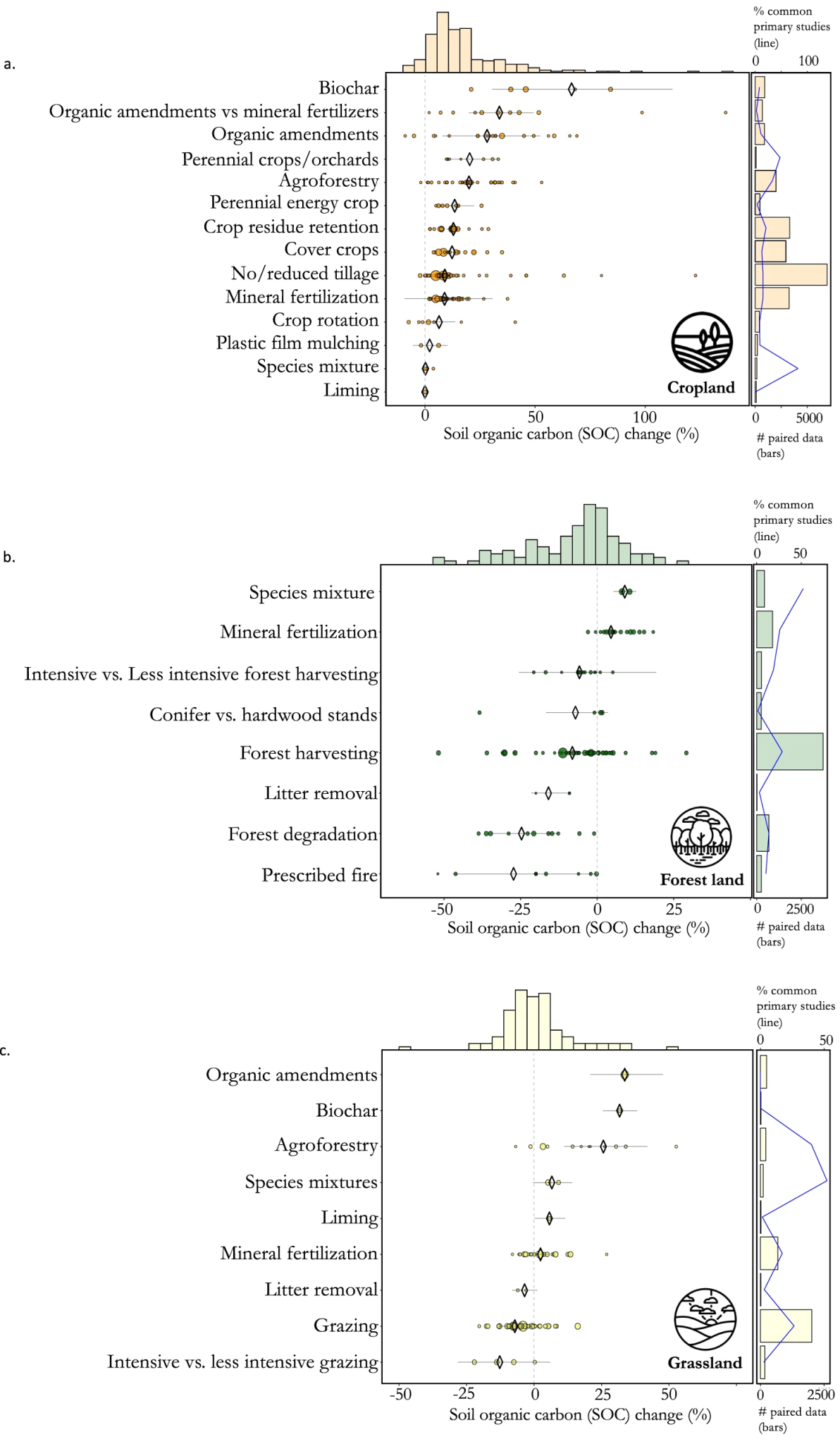
Fig. 3: Percentage change in soil organic carbon (SOC) due to land management practices
Results are detailed for for croplands (a) forest lands (b) and grasslands (c) Diamonds and lines of the main plots represent the mean effect sizes and 95% confidence intervals (CIs), respectively. The dot sizes are proportional to the number of paired data analyzed. The histograms above each plot represent the probability distribution of effects for all practices combined. The bar plots on the right side of each main plot represent the number of primary studies for each practice (bars) and the percentage of primary studies used by at least two meta-analyses (lines). Forest degradation includes the transformation of primary forest to secondary forest and secondary forest to plantation forest.





