October 20, 2022 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Source |
Introduction: The cold chain in modern food systems helps reduce food waste but increases energy use, contributing to GHG emissions. Refrigeration accounts for 1% of global GHG emissions and 15% of electricity use. To address this, phase-change material-based cold storage systems (PCCSS) offers a lower-emission alternative to traditional systems. Researchers from University of Padova in Italy and from Guangzhou University in China evaluate the carbon footprint of traditional vapor-compression refrigeration systems (VCRS) versus phase-change material-based cold storage systems (PCCSS).
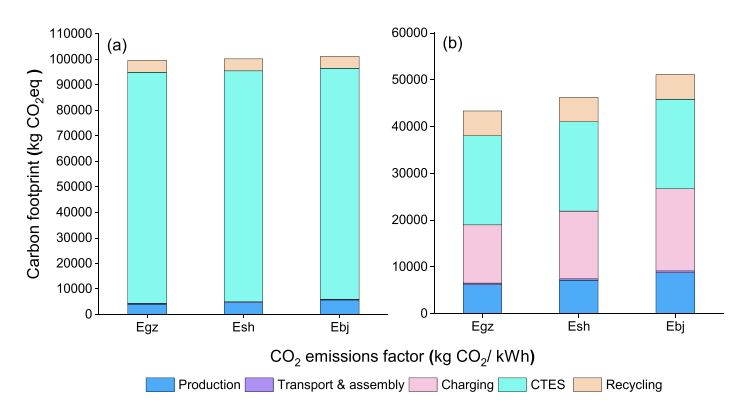
Key findings: Results show PCCSS can reduce carbon emissions by 22% to 56% compared to VCRS, especially in warmer climates. The use stage is the primary source of emissions for both systems, contributing 84%-91% for VCRS and about 68% for PCCSS. PCCSS's advantage is greater in regions with lower-emission electric grids. However, PCCSS's production and recycling stages have higher carbon footprints than VCRS. The study also highlights the importance of improving engine efficiency, utilizing cleaner electricity, and opting for low-GWP refrigerants to further reduce emissions.
Figure | The life cycle carbon footprint of both VCRS and PCCSS at three CO2 emissions factors (a, VCSS; and b, PCCSS). CTES: Cold thermal energy storage. Egz: Carbon footprint in Guangzhou. Esh: Carbon footprint in Shanghai. Ebi: Carbon footprint in Beijing.