June 1, 2024 | npj Science of Food | Source |
Introduction: An Italian research team led University of Turin investigated how food labels and consumer awareness impact sustainable eating habits and responses to climate change. By surveying 6,500 people from Italy, France, Germany, Denmark, the USA, and China, researchers examined how factors like age, gender, and country of origin influence food purchasing habits and interest in sustainable food certifications.
Key findings: Consumers' awareness of and interest in sustainability labels vary significantly. For instance, Chinese consumers showed high interest in sustainable certifications and increased consumption of fruits and vegetables. Conversely, Danish consumers, particularly older adults, reduced their consumption of meat and cheeses but showed less interest in certifications. The study also found that men generally purchased more meat, while women showed greater interest in sustainable certifications for vegetables.
Overall, while food labels can encourage more sustainable diets, many consumers still underestimate the environmental impact of their choices. This suggests that improving consumer awareness and making certifications more transparent could help drive more substantial changes in eating habits and support climate action.
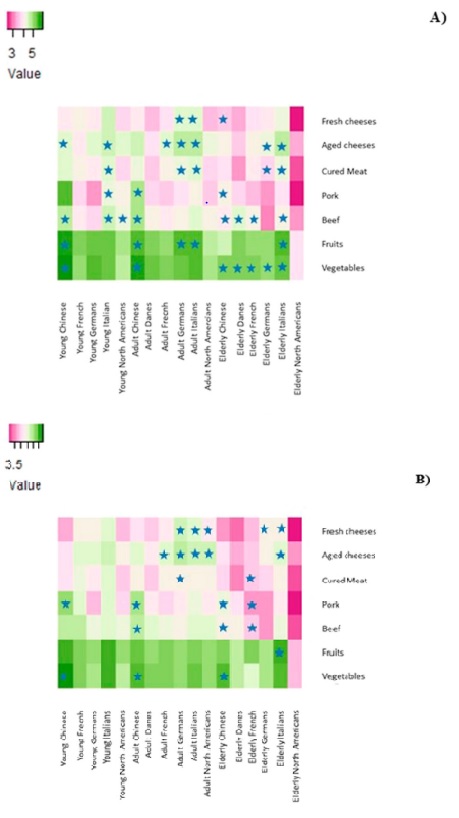
Figure | Heatmaps of the food purchase frequency, and age and country-of-origin of the consumers according to gender. A Women and (B) Men. The intensity of the colors represents the mean values of the food purchasing frequency and socio demographics according to gender. The stars represent significantly higher mean values.





