May 1, 2024 | Annual Review of Public Health | Source |
Introduction: Sustainable diets have evolved alongside the UN Sustainable Development Goals, incorporating goals in terms of agricultural productivity, diet quality, environmental footprint reduction, and social justice. Researchers from Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in the US and Aarhus University in Denmark explore the shift from animal-source foods to plant-based diets in terms of impacts on human health, ecological health, social equity, and economic prosperity, and recommend strategies for governments, businesses, and civil society to promote plant-rich diets.
Key findings: Ultra-processed foods, often unhealthy, are contrasted with minimally processed, nutrient-dense foods. Regional differences highlight the need for diverse strategies. High-income countries must reduce red and processed meat consumption, while low-income countries must ensure nutritional adequacy for vulnerable populations. National dietary guidelines must incorporate sustainability principles.
Alternative proteins (Aps) from plants, algae, fungi, and lab-grown sources are essential for reducing the ecological impact of traditional livestock. However, the healthfulness of AP products depends on their processing.
The transition to plant-based diets faces challenges in health, ecological impact, social equity, and economic viability, requiring coordinated efforts to achieve sustainable food systems by 2050.
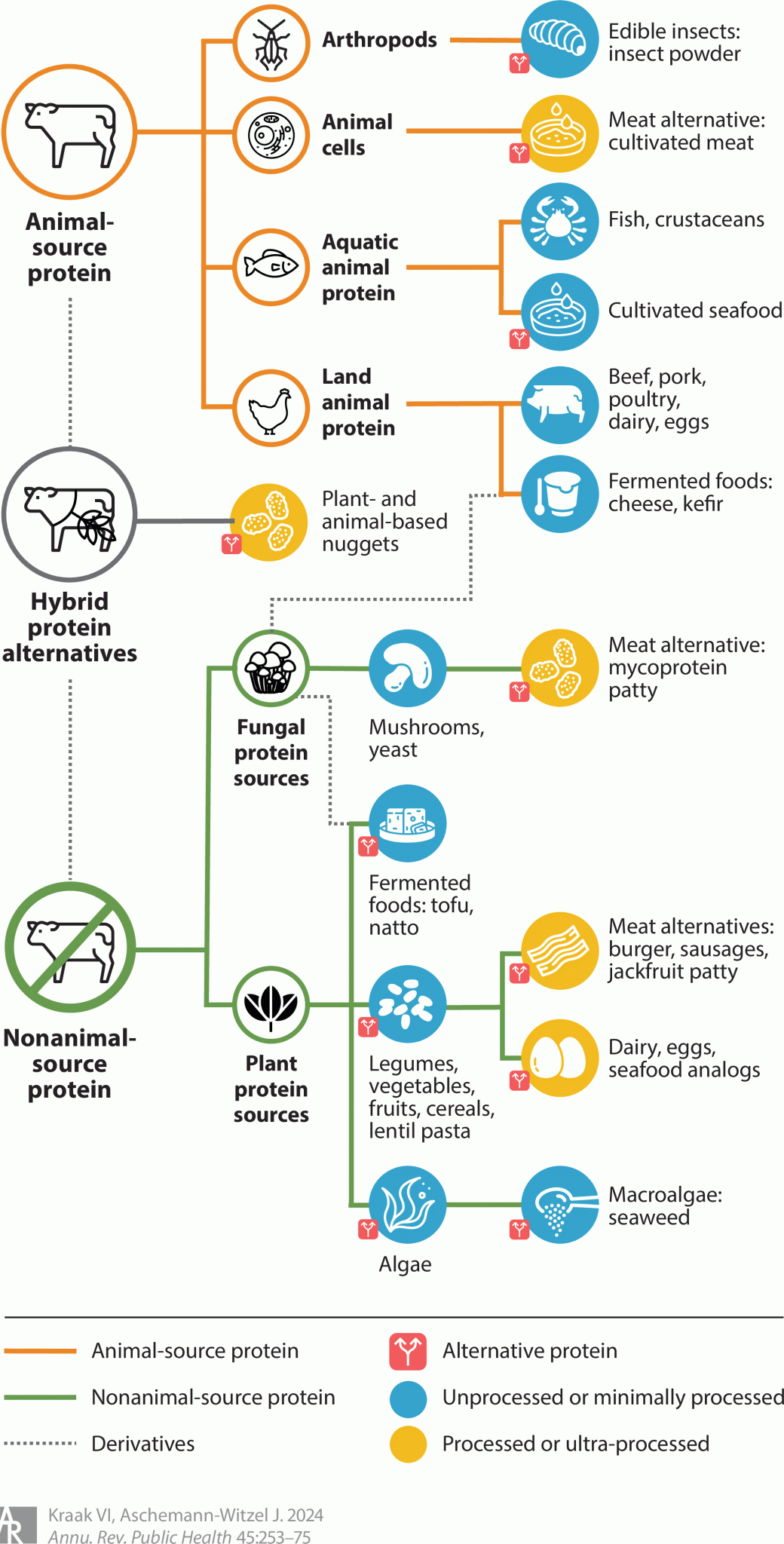
Figure | A typology of plant-, animal-, and hybrid-source proteins to encourage plant-based products that support sustainable diets.






