July 20, 2023 |Science of The Total Environment
Researchers from the University of Iowa and Grinnell College set out to investigate an essential but often overlooked aspect of agriculture: how carbon moves through fields that are artificially drained for farming.
Carbon is a crucial element that cycles naturally through the soil in agricultural areas. However, there hasn't been much research on how carbon in various forms, both organic and inorganic, moves through the soil in drained fields.
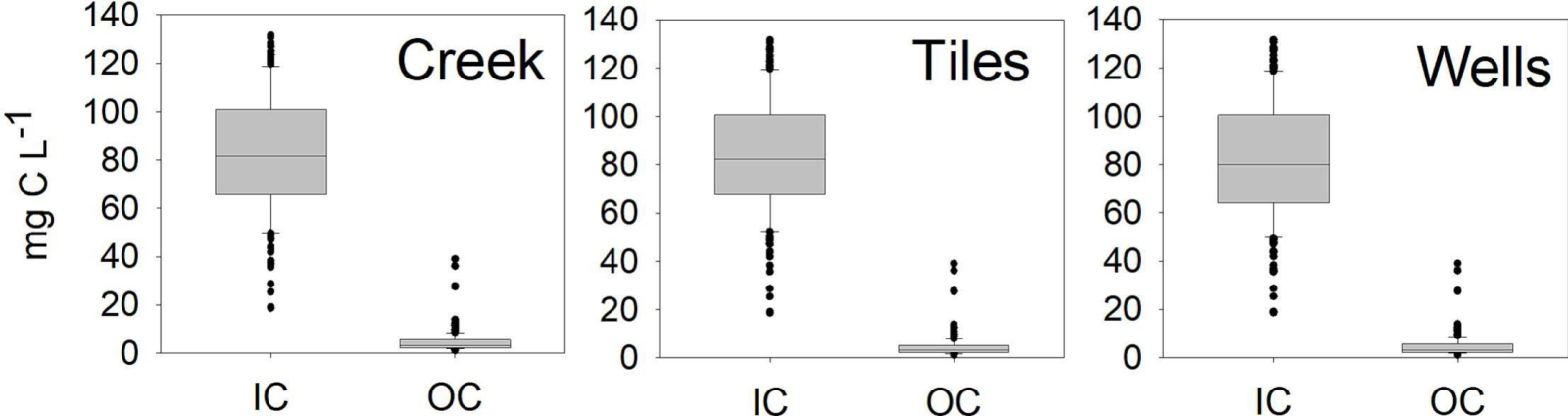
In this study, the researchers closely monitored a single cropped field in north-central Iowa during the March to November period in 2018. They focused on eight tile outlets (where excess water drains), nine groundwater wells, and the nearby stream. Their goal was to understand how inorganic carbon (IC) and organic carbon (OC) flowed from the soil to the stream.
Here's what they found:
- Carbon Dominance: Most of the carbon that flowed out of the field was in the form of inorganic carbon (IC). In fact, IC losses through subsurface drainage tiles were a whopping 20 times higher than the concentration of dissolved OC in the tiles, groundwater, and the nearby Hardin Creek.
- Subsurface Drainage: The drainage tiles, which are used to remove excess water from fields, were responsible for approximately 96% of the total carbon exported from the field.
- Carbon Stock: The researchers also dug deep into the soil, going down 1.2 meters, and found that there was a substantial amount of total carbon (TC) stored in the shallow soils. They estimated that only a small percentage of this carbon (0.23%) was lost in a single year through the drainage system.
- Mitigation Factors: It's likely that some of this carbon loss is balanced out by reduced tillage practices and the addition of lime to the soil.
The study's results emphasize the importance of carefully monitoring the movement of carbon from agricultural fields. This monitoring is crucial for accurately assessing how much carbon is being stored in the soil, which is essential for mitigating climate change. By understanding these processes better, we can improve our efforts to sequester carbon and contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly farming industry.
Read more: Dissolved inorganic and organic carbon export from tile-drained midwestern agricultural systems
Graphical Abstract